Five Customer First Rules for Retailers: the new tech edition
Customer consequences to consider when introducing new technology or services: a dunnhumby perspective by David Ciancio.
One of the most important lessons for retailers from the Covid-19 pandemic is that innovations in technologies, services, and science are more urgently required to differentiate and indeed, to survive. Customers’ increasing demands for more digital, contactless, personal, convenient, and safer shopping experiences are forcing heavier investments in enabling technologies. A tipping point has been reached that now requires more efficient solutions for ‘digital transformation’ to the shopping experience (eCommerce, mobile apps, cashier-less) as well as for store operations (efficiencies, labour savings, robotics, safety). For more discussion on this topic, please see our latest report on Customer First retailer responses for the year ahead in 2021.
How to acquire and introduce new tech and services – whether to build or buy a software solution, for example – have become even more difficult choices for a retail organisation. Typically, retailers consider factors like complexity, internal expertise, time, risk, and cost. But an organisation that aspires to be Customer First must also consider the impacts that tech and capability decisions have on their Customers. How Customers experience new technologies and services can enhance or detract from how a retailer earns greater loyalty.
To help you get it right with your Customers, here are five foundational Customer-led rules that should be applied as new technologies and services are activated for shoppers, whether built, bought, or partnered.
Five Customer First rules for new technologies and capabilities
- Whoever owns the data owns the Customer
Clive Humby, one of dunnhumby’s founders, was often quoted as advising that “data is the new oil”, foreseeing the changing economics and power of data. Today, the line between data and money is dissolving; indeed, there is a healthy economy around ‘monetising’ data, insights, exposure, and access, as the likes of Google and Amazon know very well.
In fact, this new data economy depends on ‘owning’ the relationships with Customers directly, in a way that installs the data owner as the sole agent of ‘personalised’ communications and benefits to the Customer.
Therefore, the first, and arguably most important Customer First decision when considering new technologies and services is whether the tech or capability enables a more direct relationship with the Customer through transparent ownership of the Customer data that each tech or service generates. For the purposes of this article, Customer data is defined as the information Customers provide while interacting with a business via a cash register, website, mobile applications, surveys, social media, marketing campaigns, and all other online and offline touchpoints.
Customer First organisations consider Customer data to be a gift from shoppers and steward its protection and use with gratitude and great care. Unfortunately, the same cannot be said with regards to all technologies, services, or capabilities that the organisation might introduce. Careful attention should be paid to the Customer data consequences when service intermediaries sit between a retailer and its Customers, for example, as with online shopping or media services.
Recommendations for Build, Buy, or Partner decisions regarding data ownership:
- Always own the data – and therefore the relationship – with your Customer
- The right partners are data processors who work in support of your Customer relationship, not those who become data owners themselves through their service offerings to your Customers
- Speed matters more than ever
Meeting rapidly changing Customer needs (as during the Covid-19 pandemic) has greatly accelerated the requirement for new technologies and services – like online grocery shopping with delivery or click and collect and no-contact payment apps – eliminating the luxury of time for most retailers to develop new capabilities internally from scratch.
And even prior to the pandemic, Customer needs were already changing faster than most operators typically anticipated, triggered by digital and social media revolutions, competitive disruptions, and shifting demographics.
Customer First organisations better understand and anticipate changing Customer needs using a disciplined Customer Review analytical framework in regular cadence. They are nimbly responsive to the Customer, following the shopper first rather than the market or competition first. And they then build, buy, or partner by putting Customer considerations at the front of their decision process.
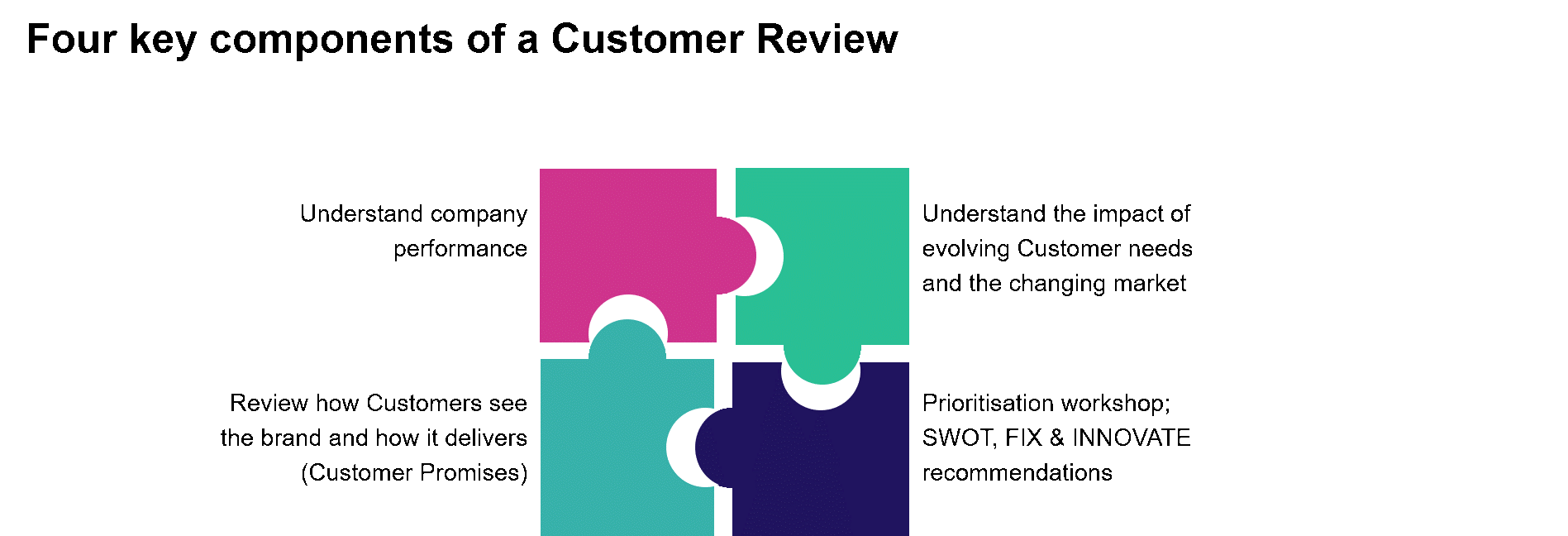
Recommendations for Build, Buy, or Partner decisions regarding speed to market:
- Better follow Customers and aim to meet their needs faster using a disciplined data-led review of shopper needs, behaviours, and market trends
- Responsiveness = selecting whichever partner (external or internal) accelerates your Customer-facing capabilities the fastest and most completely
- The more middlemen, the murkier the message
To keep pace with the breadth and depth of change mentioned above, retailers are lately turning to an increasing community of specialists in technology, data, insights, communications, coupon syndicates, loyalty platforms or coalitions, and omnichannel fulfilment or delivery providers. The result is a new form of intermediary ecosystem, like the one illustrated in the graphic below.
The challenge in such a broad intermediary layer is that every service provider typically has a different agenda, and often speaks with a different strategy or voice to the Customer than does another, or than does the retailer itself. For example, one coupon syndicate might target offers based on a brand’s strategy that may not be fully aligned with the retailer’s category strategy. This creates disparate Customer experiences of the retailer’s brand, often felt by Customers as random acts of marketing, and by the retailer as increased management costs.
Customer First organisations detail a clear Customer Strategy to align all interactions between partners or intermediaries and their strategic Customers. The forms, frequency, generosity, and voice of all communications and throughout all touchpoints are fully integrated and activated against this Customer Strategy. Hence, they partner, buy, or build with solid Customer guardrails in place.
Recommendations for Build, Buy, or Partner decisions regarding a clear Customer strategy and integrated messages to Customers:
- All Customer-facing partners must be fully aligned on a single and clear Customer Strategy to optimise the right messages and voice from a retailer
- Fewer of the right partners with the right Customer First ethos is better; too many cooks spoil the broth and confuse the Customer.

- Conspicuous or invisible to Customers?
Of course, not all tech or services in a retail ecosystem are experienced directly by Customers. For backstage processes that are invisible to Customers (such as procurement, accounting, operational systems, etc), Customer considerations are much less important in the decision to build, buy, or partner.
Customer First organisations nonetheless explore any potential impacts on Customers from each tech and capability decision, whether conspicuous or invisible to shoppers, and explore potential downstream consequences on their Customer experiences.
Recommendations for Build, Buy, or Partner decisions regarding Customer visibility:
Ask, “what will the Customer see or feel differently as a result of this new technology or service?” (thinking more about the physical experience by channel, and less about softer potential benefits in this exercise)
- Examples of invisible backend tech and services: supply chain (demand forecasting, procurement, logistics), checkout and payment platforms, ERP software, call centre software, data warehousing and security, eCommerce fulfilment systems, shopper data science, advertising / media infrastructure
- Examples of conspicuous direct Customer experiences: mobile app interfaces, loyalty offer delivery, eCommerce delivery, contactless payment interfaces, print and digital flyers
- Mindset and skillset are more important than toolset
Customers experience change in tech or services in touchpoints throughout the store, and most often through their interactions with employees who can act as explainers, recommenders, or critics of the change. Unfortunately, most organisations underestimate the importance of their Customer-facing staff in their role as advocates and ambassadors, and so sub-optimally prepare their teams for tech or services changes, whether built, bought, or partnered.
Customer First organisations manage internal culture changes in line with Customer behaviour changes. They invest in upskilling their people when investing in new technologies or services, and they create appropriate change management to win ‘hearts and minds’ in favour of the change amongst their staff and partners. Creating the right employee and partner behaviour is arguably sometimes more important than the tech when it comes to delivering a better Customer experience
Recommendations for Build, Buy, or Partner decisions regarding Customer visibility:
- To deliver on the promises from better technology or services (precisely the reason to have invested in the tech or services in the first place), a retailer must invest in upskilling and empowering its people to grow their skillset
- And, one must plan for appropriate culture change to also win a supportive mindset, toward creating the right advocacy behaviours in store
Keeping Customers in the Decision Process
In conclusion, the decision process on whether to build or buy a software solution must also consider the impacts that tech and service decisions have on Customers, mindful of likely effects on Customer experiences. Customer First retailers earn greater loyalty by applying these five rules to their decisions on which capabilities they build internally, buy or partner inside their specialist ecosystem.
For additional information on Customer First principles and frameworks, or guidance on building a clear Customer Strategy and activating an effective Customer Review, please contact your dunnhumby representative.
The latest insights from our experts around the world
Understanding evolving customer needs in the age of AI and data abundance


